Give Feedback What do you think of p value calculator?
 Worst
Worst
 Poor
Poor
 Average
Average
 Good
Good
 Excellent
Excellent
This P value calculator is a calculus tool that helps to compute the probability level using the test value, degree of freedom, and significance level.
You can find the significance level of p-values through this calculator using different hypothesis tests e.g from t value, z score, and chi-square.
Definition of p-value is:
“The probability of getting a sample similar or extreme than our estimated data under the null hypothesis.”
In simple words, how probable or how likely it is that one gets the same sample data as we just got from the experiment, considering the null hypothesis is true.
P-value can be easily calculated using the P value calculator above. However, for a good understanding, each step to find the p-value manually is explained in detail below:
Below are the steps that help you to find the p-value:
To calculate the p-value using test statistics, follow the below steps:
You can find the p-value from the z score by the following formula:
p-value = 2 * (1 - Φ(|z|))
Where Φ(x) is the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution evaluated at x.
This formula is for a two-tailed p-value. For left and right-tailed tests are given below:
Example:
A consumer rights company wants to test the null hypothesis i.e a nuts pack has exactly 78 nuts against the alternative hypothesis i.e nuts are not 78.
For a sample of 100 packets, the mean amount of nuts is 76 with a standard deviation of 13.5. While the population mean is 80. Find the probability value for a two-tailed test.
Solution:
Step 1: Write both hypotheses.
h0 = a pack contains 78 nuts
ha = a pack does not contain 78 nuts
Step 2: Write the data for test statistics.
n = 100
͞x = 76
s = 13.5
μ0 = 80
Step 3: Find the z score value.
(Since the sample size is greater than 30, population and sample standard deviations are the same.)
Using the formula;
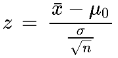
z = (76 - 80) / (13.5/√100)
z = -4 / 1.35
z = -2.96
Step 4: Look for this value on the z-table.
The value for -2.96 is 0.0015. But since the test type was two-tailed, you will have to multiply this value by 2 to get the area under the curve for both tails.
= 2 x (0.0015)
= 0.003
This p-value is less than the standard significance level i.e 0.05. Therefore not enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis.
